
Introduction
Crypto exchanges aren’t just digital marketplaces they’re modern-day treasure vaults. And just like vaults attract robbers, crypto exchanges draw hackers from across the globe.
In recent years, we’ve seen attacks on Mt.Gox, Wazir X, CoinEx, KuCoin, DDM Bitcoin, FTX, CoinCheck, And Bybit leading to losses worth billions. These incidents have left both investors and exchange operators shaken and they’re only growing more frequent.
So, why are crypto platforms so vulnerable? And more importantly, how can founders, CISOs, and technical leaders prevent their platforms from becoming the next headline?
In this article, we’ll break down how hackers exploit crypto systems and give you real, actionable ways to protect against those threats.
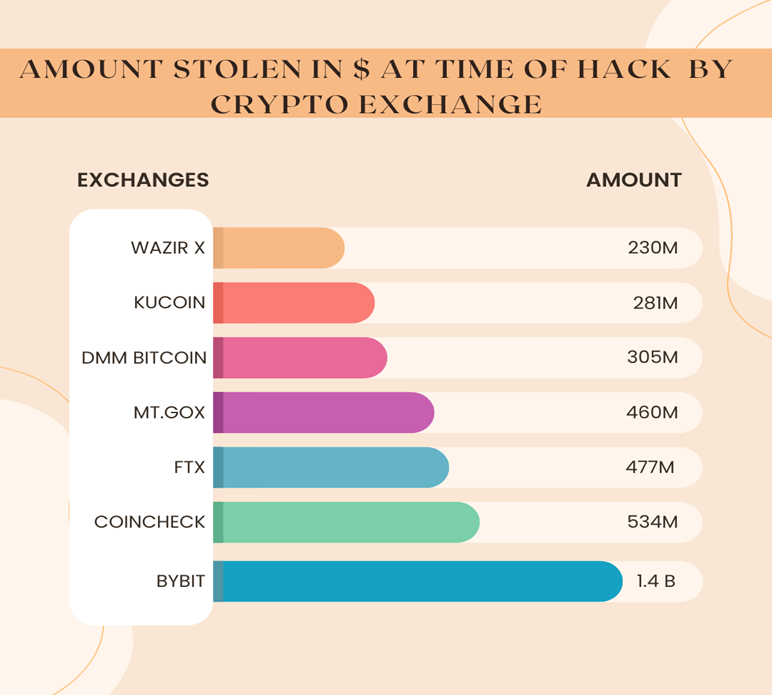
Why Are Crypto Exchanges a Prime Target for Hackers?
Let’s talk about why these platforms are on every cybercriminal’s radar. It comes down to one thing: value.
Crypto exchanges handle enormous sums of money in the form of digital assets. Unlike banks, which have decades of security investment and insurance frameworks, many crypto firms are still playing catch-up.
The architecture of most exchanges is decentralized or modular, which can leave gaps between systems. Security isn’t always consistent across APIs, wallets, cloud services, and apps.
Compliance also varies drastically from one region to another, making it hard to apply a universal standard of protection. Add to that the human element users falling for phishing scams, or employees with too much access and the vulnerabilities multiply fast.
According to Chainalysis, hackers stole over $3.8 billion in crypto in 2024 alone, with a significant chunk coming from centralized platforms. That stat should be a wake-up call.
Common Attack Vectors Used by Hackers
Hackers don’t need to be magicians. They just need one open door.
Let’s walk through the most common ways they break in.
Phishing and Social Engineering are still among the top causes of compromise. Attackers create fake login portals, impersonate customer support agents, or send malicious links that trick users or employees into handing over credentials.
This is exactly what happened in some parts of the Bitfinex saga. Even social media scams involving crypto giveaways have fooled millions.
Then there are API exploits. Many exchanges expose APIs for trading bots and user functions. But if these endpoints aren’t secured, hackers can exploit them.
A missing authentication step or poor rate limiting can lead to account takeover or data leaks. APIs should never be treated as low-risk surfaces.
Private key theft is another major concern. Whether it’s a hot wallet connected to the internet or a compromised employee’s laptop, leaked keys can result in irreversible theft.
Some attacks come from insiders, others from poorly secured infrastructure or malware that exposes access credentials.
In DeFi Decentralized finance, smart contract exploits are a popular route. Hackers look for logic bugs or re-entrancy flaws in the code. Flash loan attacks, where hackers borrow large sums and manipulate liquidity, have caused major damage in just seconds.
Don’t forget about cloud misconfigurations. Leaving an AWS S3 bucket public, or failing to restrict root access, is an open invitation for data exfiltration or worse.
We’ve also seen malware, like clipboard hijackers, that change copied wallet addresses. Remote Access Trojans (RATs) can silently spy on internal systems and exfiltrate secrets.
Finally, DDoS and ransomware attacks can cripple operations. These attacks disrupt services and force companies to pay up or lose access entirely.
How to Prevent Crypto Exchange Attacks: Best Practices
Prevention doesn’t happen by accident. It requires a clear, layered defence strategy.
Start by adopting a Zero Trust architecture. This means no user or system gets blind trust. Use micro segmentation to limit exposure and apply strict access controls.
These controls should be especially enforced around wallets, APIs, and backend systems with sensitive permissions.
Next, conduct regular penetration tests. Hiring ethical hackers to break into your system before real ones do can reveal blind spots.
You can also launch bug bounty programs through platforms like Hacker One or Immune. These programs incentivize white-hat hackers to find flaws before malicious actors do.
Don’t overlook API security. Every endpoint needs to be authenticated, rate-limited, and monitored for anomalies.
Use an API gateway and implement OAuth with proper token scopes and expiry logic. Secure documentation should also never be publicly accessible.
For storage, move as many funds as possible to cold wallets. These are systems that are kept offline and are far harder to breach remotely.
Use multi-signature wallets so that no single person can move assets without approval. This reduces insider risk significantly.
Your team should have real-time monitoring tools in place. SIEM platforms can help detect and respond to anomalies as they happen.
Pair that with external threat intelligence feeds to enhance context and accelerate your response.
Train your staff regularly. Even your most technical team members can fall for a well-crafted phishing email or deepfake call.
Run social engineering simulations, and enforce 2FA across all accounts, including internal admin systems.
If you’re working with smart contracts, make audits non-negotiable. Use credible firms like Certik or ConsenSys Diligence to review your code before anything goes live.
⚖️ Compliance Measures Exchanges Should Follow
Good security is more than just code it’s also about compliance. Frameworks like SOC 2 Type II or ISO 27001 enforce internal discipline and operational consistency.
Getting certified helps reassure partners, regulators, and users that your systems are secure and audited.
If you’re operating globally, the FATF Travel Rule requires you to collect and share certain transaction metadata. This is meant to prevent money laundering and terrorist financing.
You’ll also need to meet AML and KYC obligations, depending on your licensing jurisdiction. These rules are evolving fast and vary from region to region.
Platforms operating in the EU must also follow GDPR, especially when it comes to how and when you report data breaches.
Taking compliance seriously doesn’t just reduce risk. It builds long-term trust and positions you as a stable player in a volatile market.
What to Do If You’ve Been Breached (Post-Incident Response)
Even with strong defences, no system is bulletproof. If your exchange is breached, speed and transparency are key.
First, notify your users immediately don’t wait for the story to leak or social media to explode. Clear and fast communication builds credibility.
Freeze affected wallets or systems and rotate access keys. Limit all account operations until you’ve assessed the full scope of the breach.
Bring in blockchain forensics experts to trace where the assets went. This can help recover stolen funds or even identify the attackers’ methods and wallets.
You’ll also need to report the breach to regulators. This might include the SEC, financial crime units, or data protection agencies, depending on your location.
Be transparent. Share what happened, what you’ve learned, and what steps you’re taking. Companies that hide hacks lose trust; those that own the narrative tend to recover stronger.
Final Thoughts: Prevention Is the Best Protection
Crypto exchanges are evolving fast. But so are the threats they face.
You can’t afford to wait for a breach to take security seriously. Hackers are looking for the weakest link and if you don’t close the gaps, they will find a way in.
The good news? You don’t have to figure it all out alone. Working with a specialized cybersecurity consulting firm like us can help you build smarter defences and ensure you’re fully compliant.
If you’re unsure where your exchange stands today, start with a cyber risk assessment With Us www.securis360.com. The first step in avoiding disaster is knowing where you’re vulnerable.


