In an increasingly connected world, organizations face growing pressure from cyber threats. Systems are rarely perfect, and attackers only need one weakness to exploit. That’s where VAPT (Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Testing) comes in — these tools help you proactively find vulnerabilities before they become serious breaches. They don’t just show where cracks are; good tools also simulate real-world attacks to estimate how bad the damage could be.
By 2025, the VAPT landscape continues evolving, with many mature tools plus some newer ones adapting to cloud, mobile, and AI-powered threats. This guide lists 20 of the the most reliable VAPT tools, covering everything from networks and web apps to cloud infrastructure and mobile apps.
What is VAPT?
Vulnerability Assessment is the process of scanning systems, networks, or applications to identify known weaknesses, misconfigurations, or missing patches.
Penetration Testing builds on that by exploiting those vulnerabilities in a controlled way, to see how far an attacker could go and what damage they might do.
Together, VAPT gives a holistic view of your security posture: known issues plus the real-world impact.
What to look for in a good VAPT tool in 2025
When selecting tools, consider these factors:
- Scope: Do you need web, network, mobile, or cloud testing? Some tools specialize, others attempt to be more general.
- Automation vs Manual capabilities: Some tasks can be automated (scanning), while penetration testing often benefits from manual exploitation and analysis.
- Customization/plugins: Good tools let you add or modify modules, plug-ins or scan templates so you can adapt to new threat scenarios.
- False positives & accuracy: A tool that reports too many false positives wastes effort. Accuracy is important for actionable results.
- Integration: Does the tool integrate with CI/CD pipelines, or other security workflows (e.g. reporting, asset management)?
- Compliance & reporting: Many organisations need audits for standards (GDPR, PCI-DSS, HIPAA, etc.). Tools that provide compliance checks and clear reports help.
- Usability & support: A good UI, documentation, and vendor or community support make adoption smoother.
Top 20 VAPT Tools for 2025
Here are 20 tools that are widely used (or trending) in VAPT workflows in 2025, each with a short description of strengths + use cases:
1. Burp Suite



Use case: Web application penetration testing
Strengths: Proxy / repeater to intercept and modify HTTP requests, automated scanning plus manual manipulation. Good plugin ecosystem, supports automating targeted probes.
Why it matters in 2025: Still an industry standard for manual + automated web testing workflows.
2. Netsparker
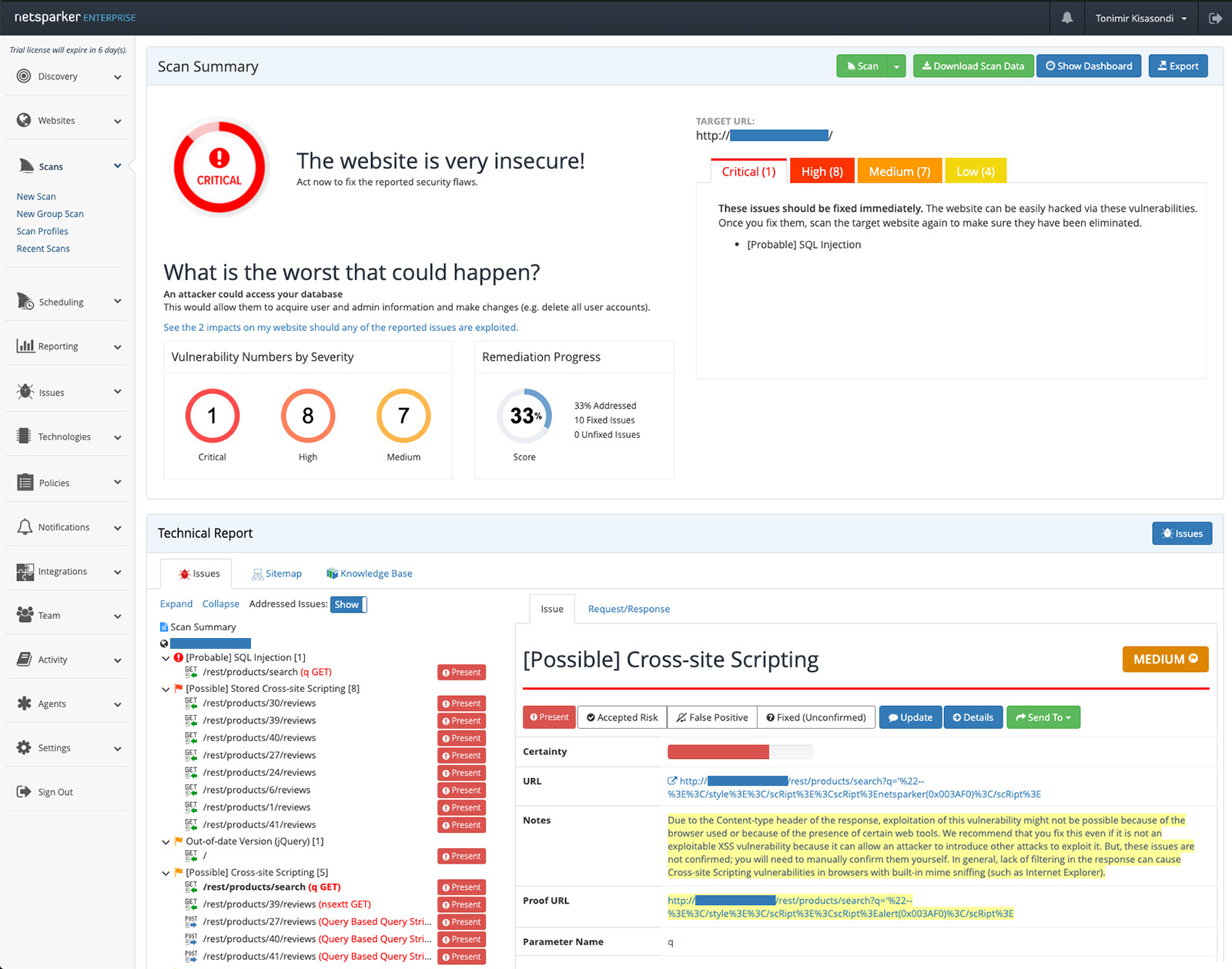


Use case: Web app vulnerability scanning
Strengths: Uses proof-based scanning to reduce false positives. Good integration with CI/CD pipelines, scalable for larger web apps.
Why it matters: Organizations want more accuracy and fewer false alarms, so tools like this are valuable.
3. OWASP Zed Attack Proxy (ZAP)



Use case: Web application scanning (passive & active)
Strengths: Open-source, supports both passive scanning (observing traffic) and active scanning (probing). Extensible with plug-ins.
Why it matters: Good free / open tool for teams doing both automated and manual assessment.
4. w3af



Use case: Web application vulnerability scanning / attack framework
Strengths: Modular design with many plug-ins, ability to run repeated scans or scripts, flexible.
Why it matters: Useful for teams who want to adapt scanning for evolving threats or custom tests.
5. SQLMap
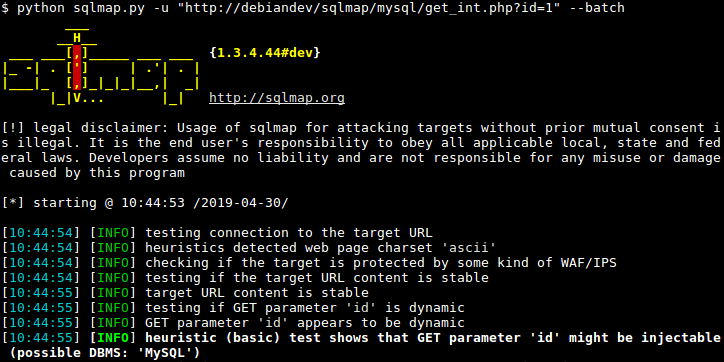

Use case: Testing for SQL injection vulnerabilities in web or database applications
Strengths: Automates detection and exploitation of SQL injection across different DB engines, can extract or manipulate data.
Why it matters: Databases remain a frequent target; automated tools like this speed up identifying injection weakness.
6. Nmap
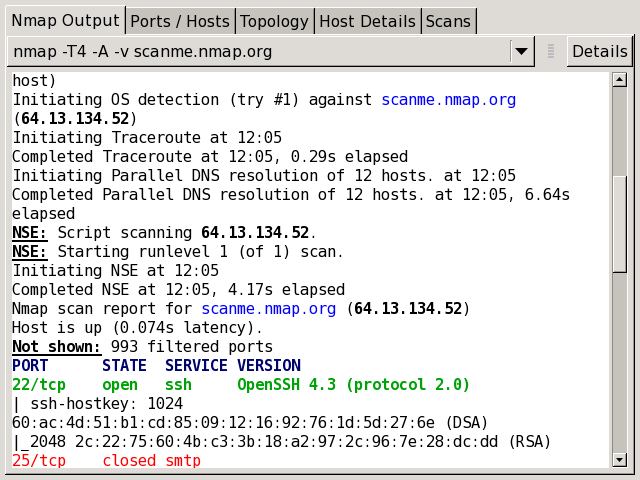
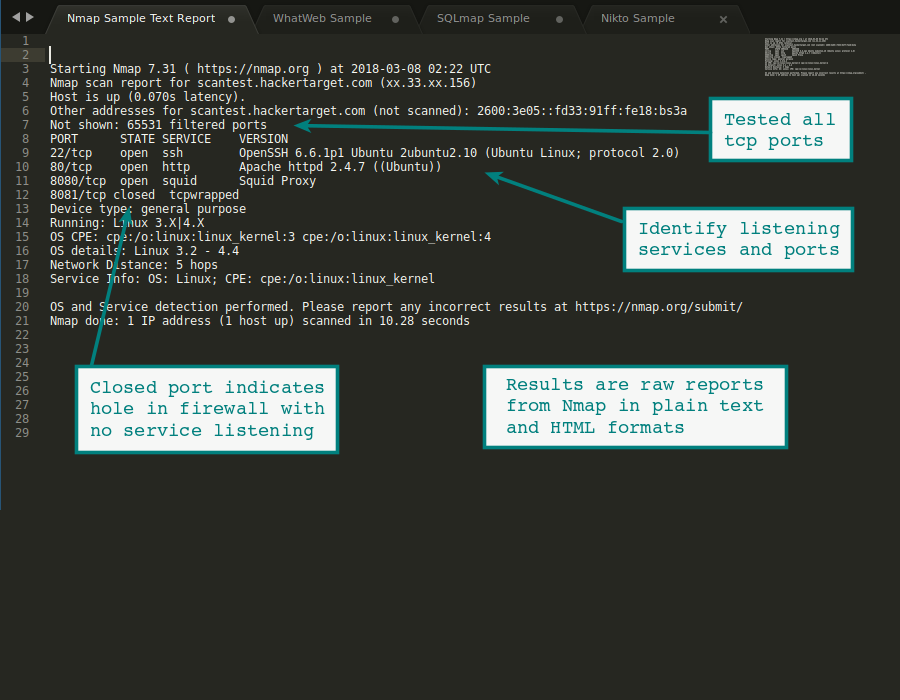
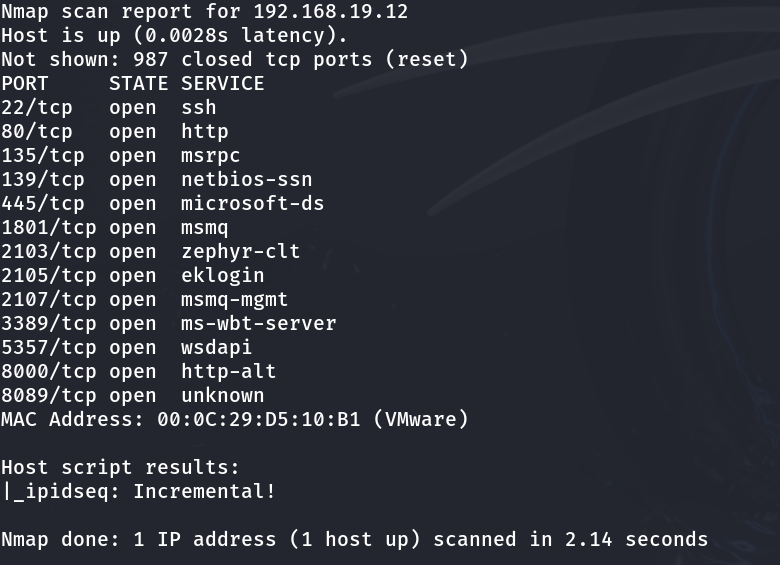
Use case: Network discovery, port scanning, host and service enumeration
Strengths: Detects open ports, OS, service versions, helps map networks and identify possible entry points.
Why it matters: Good baseline for network vulnerability scanning, discovering what’s exposed.
7. Nikto
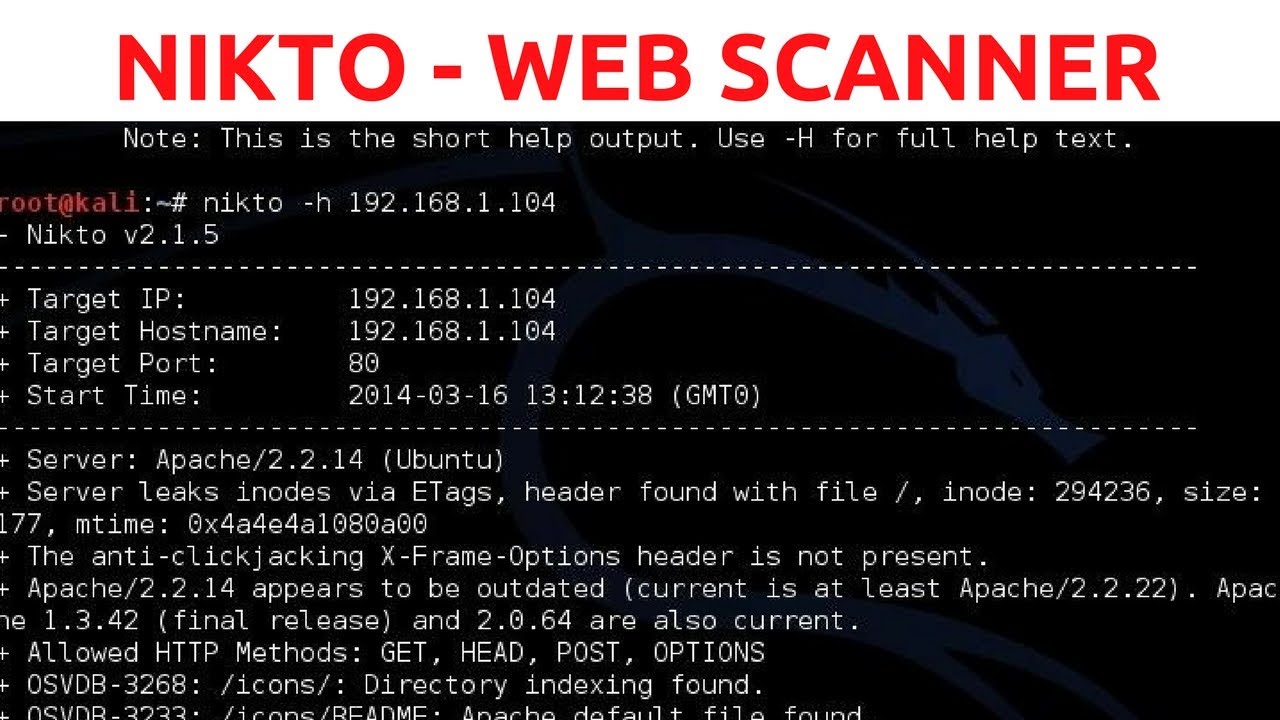
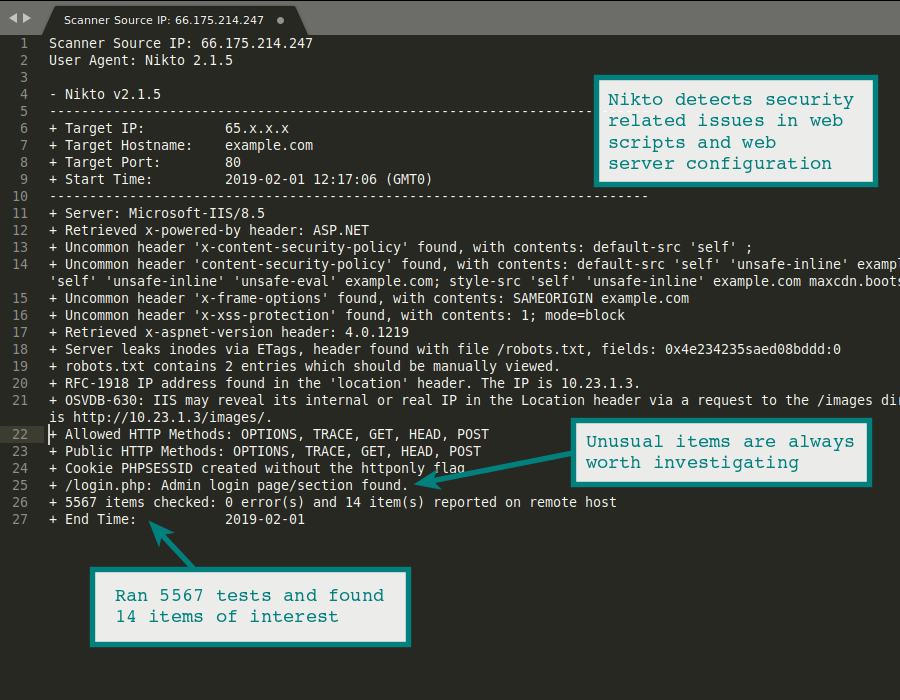

Use case: Web server scanning (misconfigurations, unsafe files, outdated software)
Strengths: Checks for dangerous files, misconfigurations, old server software versions, SSL issues.
Why it matters: Good for auditing web servers quickly; helps identify basic but often overlooked risks.
8. OpenSSL
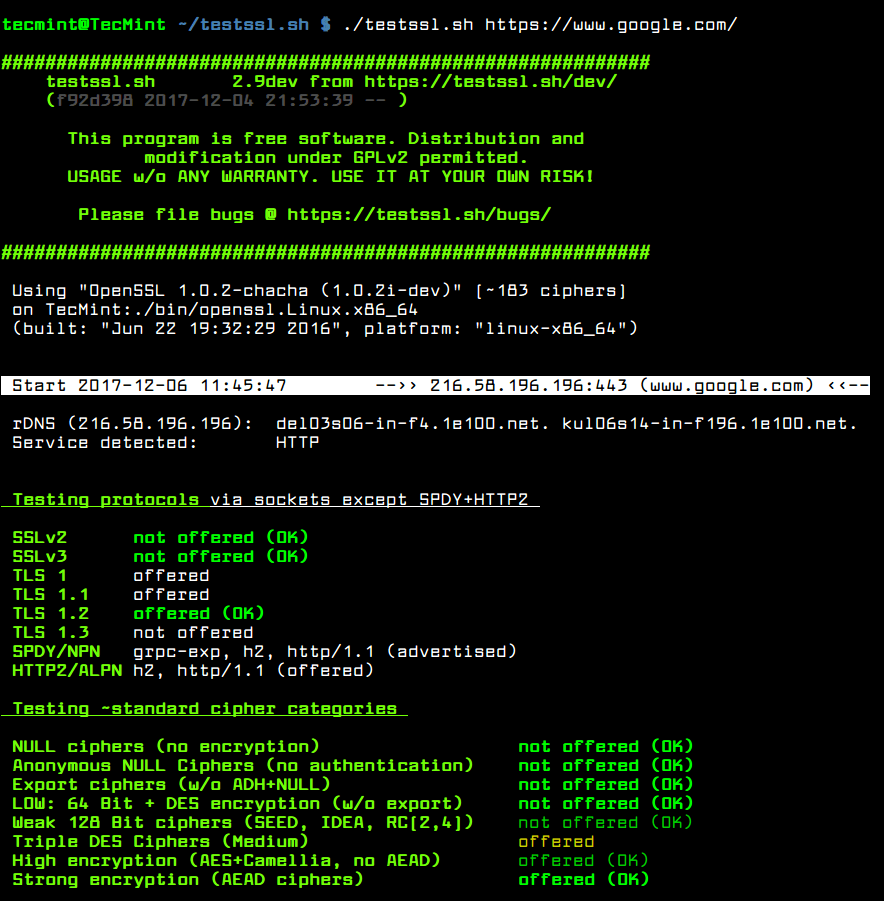

Use case: Managing SSL/TLS, encryption, cryptographic operations
Strengths: Tools for certificate creation, encryption / decryption, testing TLS configurations and certificate verification.
Why it matters: Ensuring that encryption channels are properly configured is still essential for network / application security.
9. Metasploit Framework
Use case: Penetration testing / exploit framework
Strengths: Large exploit library, post-exploit modules, ability to chain attacks after initial compromise.
Why it matters: Useful for simulating real attacks and seeing how far an attacker might go.
10. MobSF (Mobile Security Framework)



Use case: Mobile application security testing (Android / iOS)
Strengths: Performs both static code analysis and dynamic testing of mobile apps, includes API testing and malware detection.
Why it matters: Mobile continues to be a critical platform; mobile apps often have unique vulnerabilities.
11. ApkTool

Use case: Decompiling Android applications
Strengths: Extracts code and resources from Android APKs, lets testers modify and repackage apps or analyze them.
Why it matters: Helps security testers audit Android apps, see internal workings, resource usage, or suspicious code.
12. Frida

Use case: Runtime instrumentation of mobile / desktop / server apps
Strengths: Hook into live running code, modify behavior in real time, script APIs and functions for testing.
Why it matters: Very useful for reverse engineering or dynamic analysis of apps (mobile or desktop), understanding runtime behavior.
13. Drozer
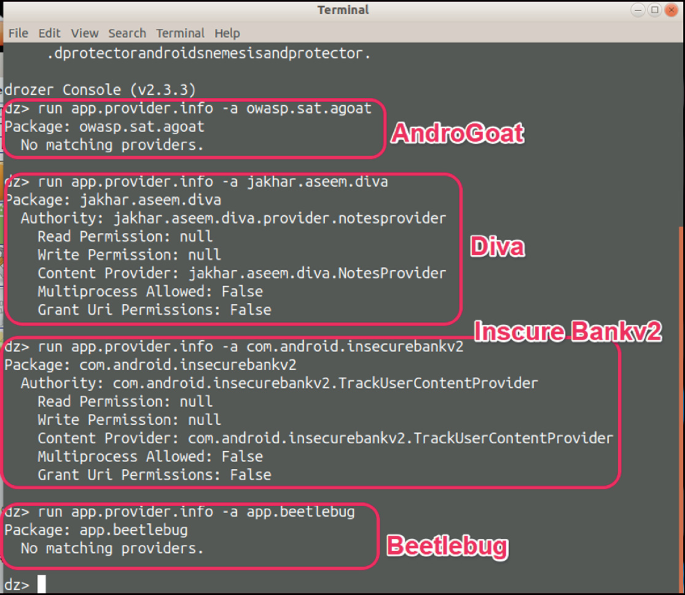
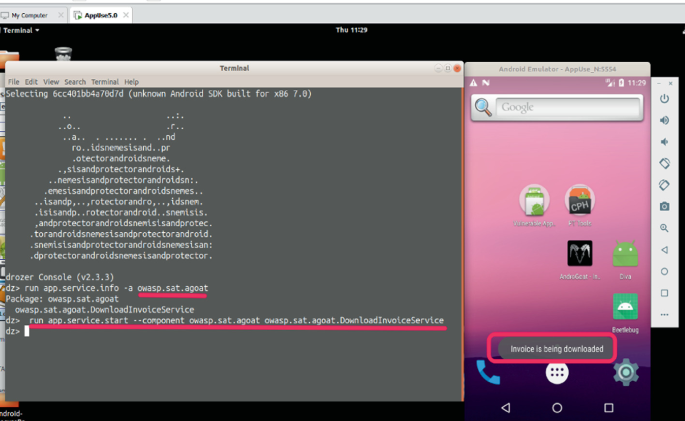
Use case: Android application and device security testing
Strengths: Allows interaction with Android apps / OS to explore security configuration, privileges, data access.
Why it matters: Useful for testers focusing on Android apps / assessing device / app permissions.
14. QARK (Quick Android Review Kit)

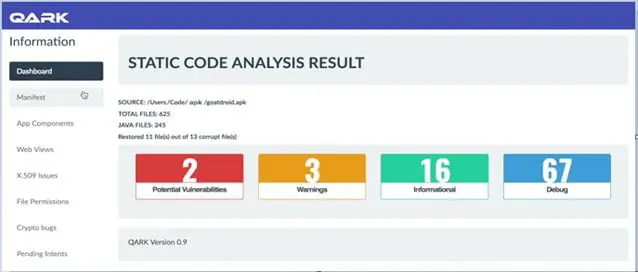
Use case: Static analysis of Android native applications
Strengths: Scans source code / byte code to detect common Android vulnerabilities, can generate proof-of-concept exploits.
Why it matters: Good for developers or testers wanting to detect weaknesses early in app development.
15. Prowler
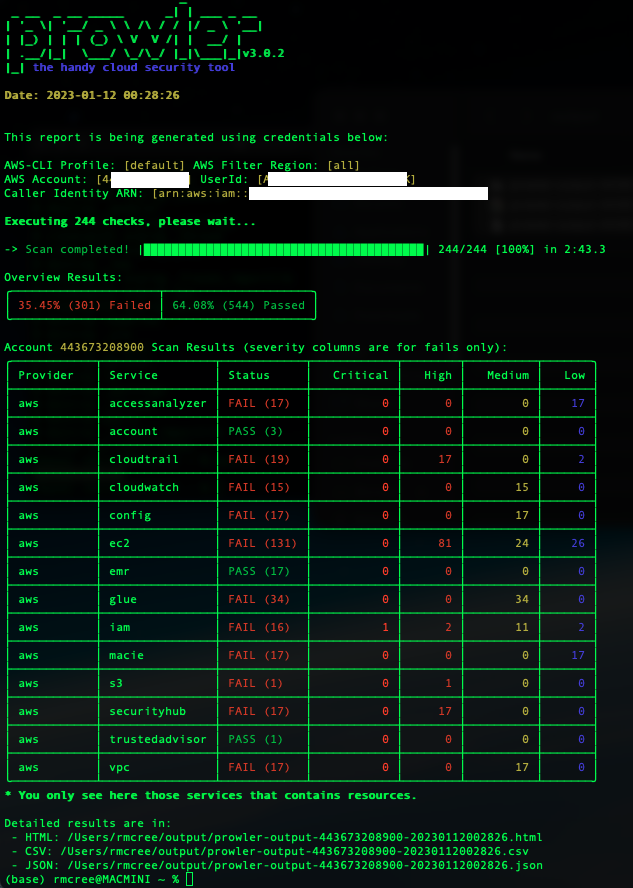

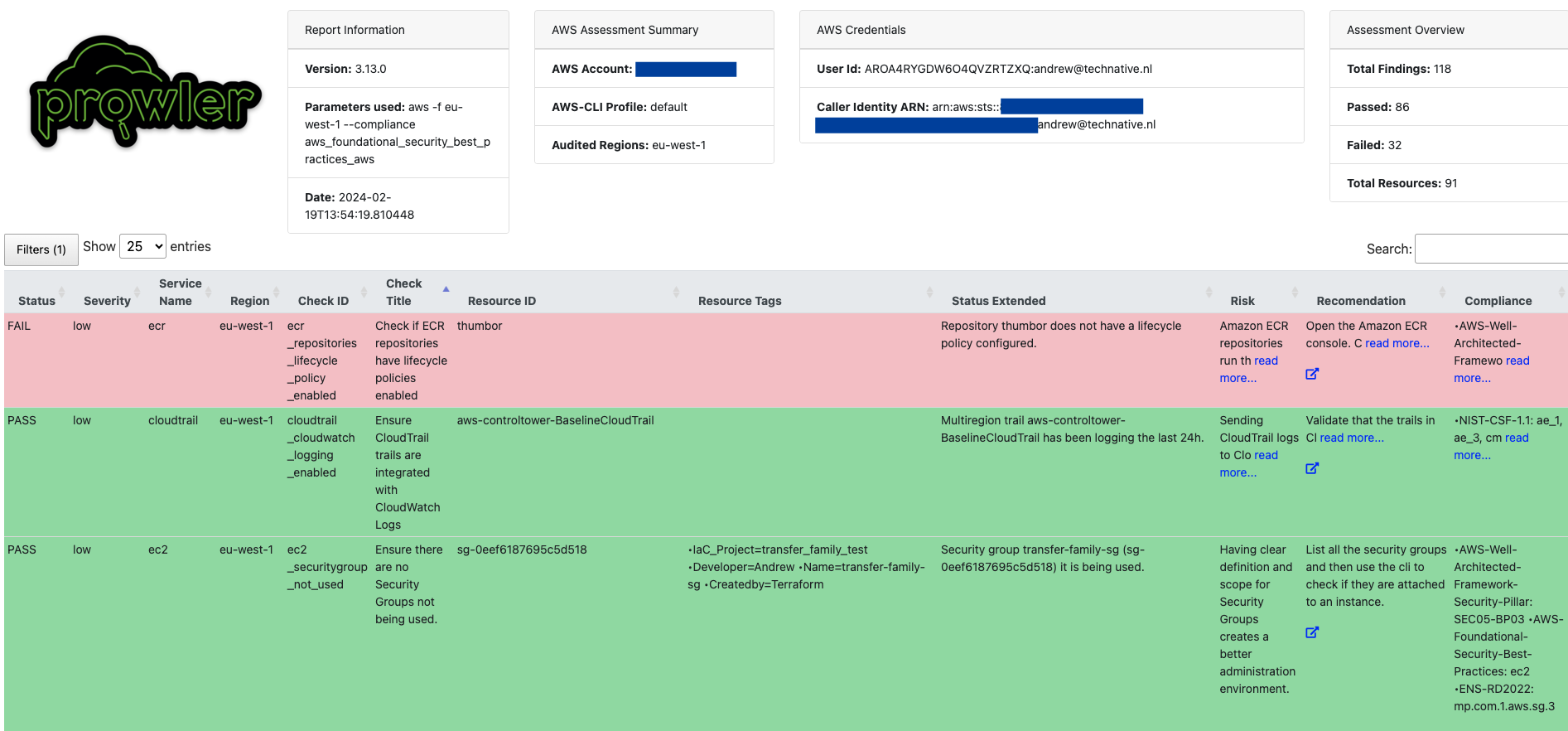
Use case: Cloud security testing (especially AWS)
Strengths: Performs many checks on AWS accounts (configurations, IAM, S3 buckets etc.), compliance auditing (CIS, GDPR, HIPAA).
Why it matters: More organizations run workloads in cloud; cloud misconfigurations are big risk surfaces.
16. Nessus
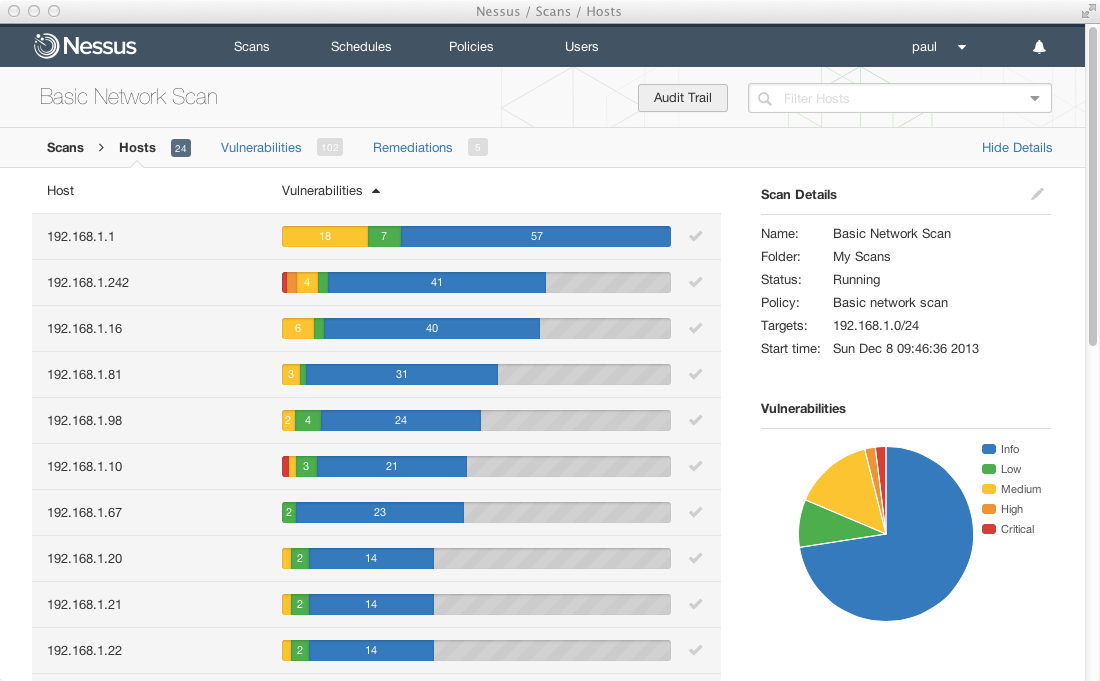

Use case: Broad vulnerability scanning (networks, devices, systems)
Strengths: Large plugin library, can scan many asset types, good reporting.
Why it matters: Still one of the trusted commercial / professional standards for vulnerability scanning.
17. CloudBrute


Use case: Enumerating cloud resources across multiple providers
Strengths: Can discover unreachable or unmonitored cloud resources, supports multiple cloud platforms.
Why it matters: Helps find hidden resources that might be misconfigured or unprotected.
18. PACU
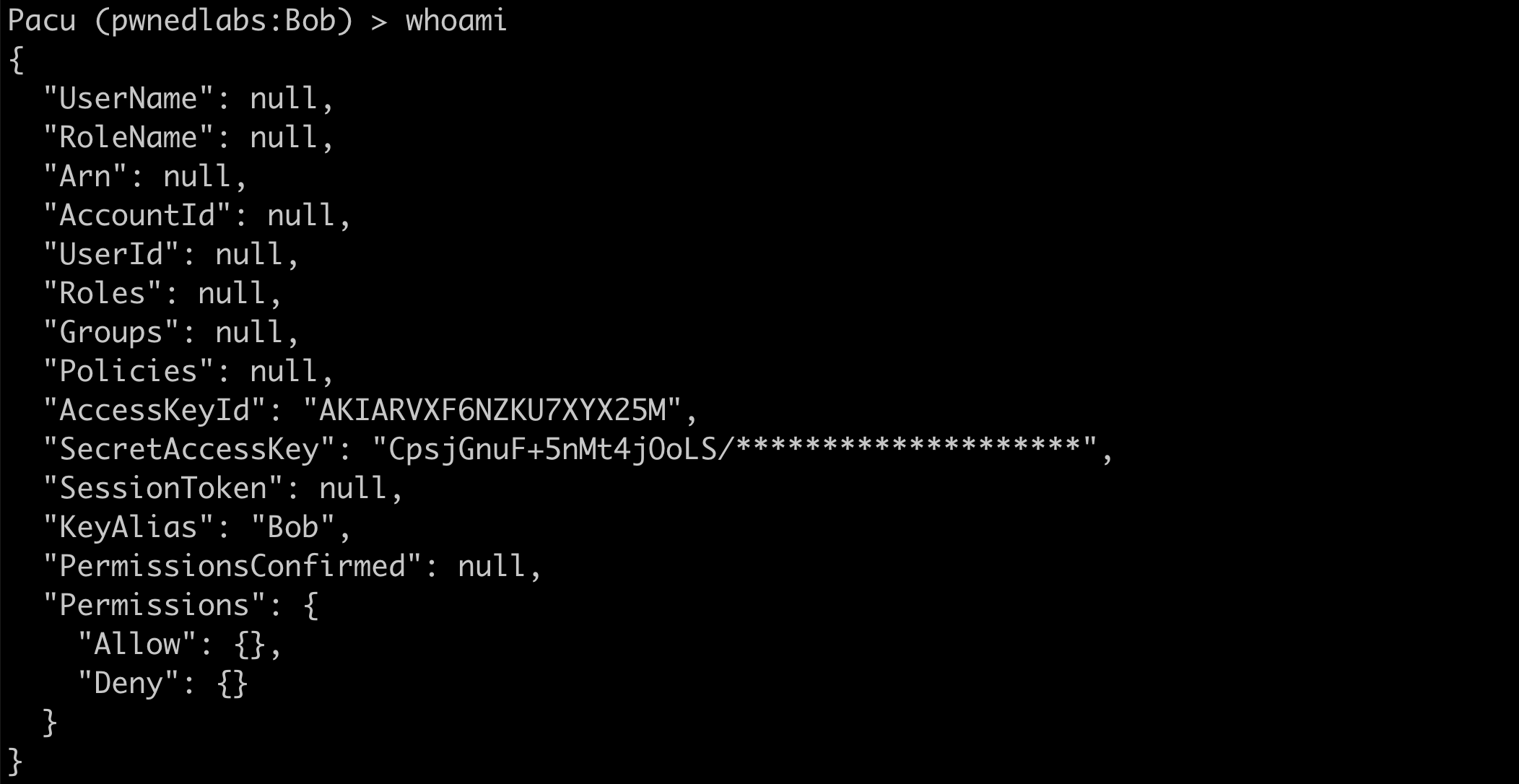


Use case: AWS penetration testing and exploitation
Strengths: Attack modules specifically for AWS services, can test configuration errors or exploit misconfigurations.
Why it matters: Very useful for red teams or security audits on cloud infrastructure to simulate real attacker behavior.
19. Yaazhini



Use case: Automated mobile application security testing (Android + iOS)
Strengths: Cross-platform mobile app vulnerability detection, automatic scanning, daily reports.
Why it matters: Mobile apps are major attack surfaces; automated tools help maintain ongoing security checks.
20. Wireshark
Use case: Network packet capture / analysis
Strengths: Captures network traffic, analyses many protocols, supports real-time capture and offline analysis.
Why it matters: For network security, it’s indispensable to understand traffic flows, detect anomalies or suspicious traffic.
Tips for using this tool set wisely
- Combine scanning tools (vulnerability scanners, network mapping) with manual exploitation to verify real risk.
- Use automation to run regular scans (e.g. daily/weekly) especially on cloud / mobile assets that change often.
- Keep your toolkits updated: exploit modules, vulnerability definitions, plug-ins.
- Build into your CI/CD pipeline where possible, so vulnerabilities get caught during development rather than after release.
- Prioritize remediation based on risk + impact, not just vulnerability count (some low severity vulnerabilities are less critical).
Conclusion
Cyber threats are not waiting. VAPT tools let you proactively find and exploit weaknesses before real attackers do. The 20 tools above span web, network, mobile, cloud, and exploit frameworks — giving you a well-rounded toolkit. Whether you’re a security engineer, app developer, or cloud red team, using the right combination of these tools can help you strengthen your defenses in 2025 and beyond.


